What Are Ketones?
Ketones are acids that the body makes when it burns its own fat. They’re made when glucose, the primary energy source, is short in supply. This occurs overnight or during dieting or fasting.
The liver converts fatty acids into ketones, which are then released into the bloodstream for use as energy. In people with diabetes, high levels of ketones in the blood can result from taking too little insulin, and this can lead to a particularly dangerous condition known as ketoacidosis.
Ketoacidosis is very risky for someone with Type 1 diabetes because they can develop dangerous levels of ketones. Ketoacidosis can also occur in someone with Type 2 diabetes if there is a major increase in insulin resistance, such as from an infection or treatment with steroids, or a reduction in insulin release from the pancreas.
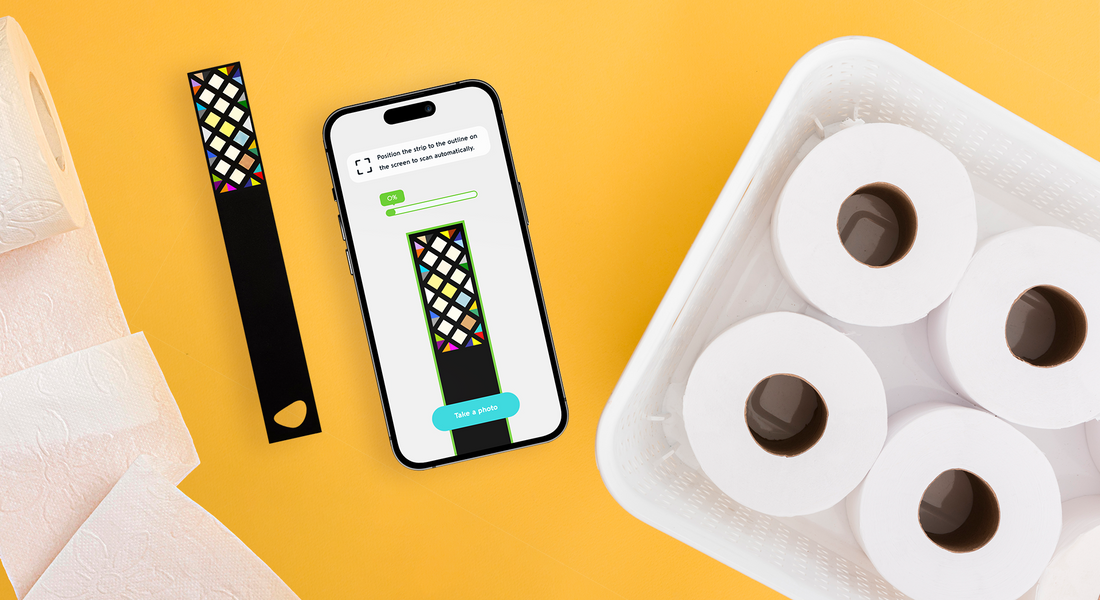
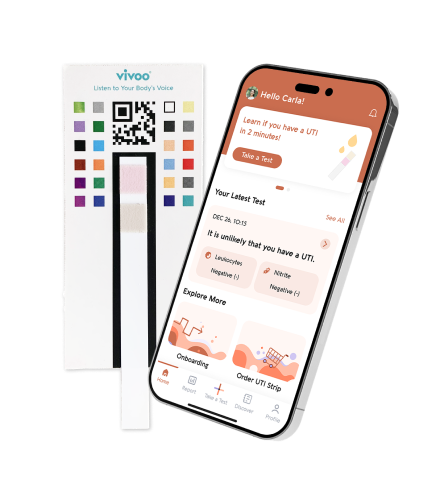
Ketones can be tested by blood or urine. You can quickly check the ketone levels in your urine with Vivoo strip.
What Causes Ketones in Urine Without Ketosis?
Ketones in the urine can be caused by several factors. These may include:
1) Diet

Dietary Preferences: People who are not on a ketogenic diet but prefer high fat and low carbohydrate foods may have ketones in their urine.
Fasting: In a person without diabetes, ketone production is the body’s normal adaptation to starvation. Starvation starts when you haven’t eaten for a prolonged period of time, for example 14-20 hours. This can occur at night or when fasting.
Eating disorders: Anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa can also cause ketones to appear in the urine. In these individuals, starvation is one of the causes of severe ketoacidosis, even when the patient denies diet restriction.
2) High Amounts of Exercise

Post-exercise ketosis was first described by Forssner. When someone overtrains, the need for respiratory fuel increases, and blood-glycerol and plasma-free fatty acid (FFA) levels rise. The increased concentration of FFA and the depletion of glycogen cause an increased rate of ketone body formation in the liver. During exercise, the extra ketone bodies serve as fuel for respiration and don’t accumulate. After exercise, the raised concentration of FFA results in post-exercise ketosis.
3) Excessive Alcohol Consumption

Drinking too much alcohol is another reason for ketones in the urine. Alcoholic ketoacidosis can develop when you drink excessive amounts of alcohol for a long period of time. The overconsumption of alcohol often causes an inadequate intake of nutrients as meals may be eaten irregularly. People who drink too much may also vomit, further depleting the body of nourishment. Not eating enough or vomiting can lead to periods of starvation, which can then lead to alcoholic ketoacidosis.
4) Other Factors
Other causes of ketones in urine are:
- illness or infection
- pregnancy
- fever
- medications, such as corticosteroids and diuretics
- prolonged vomiting and diarrhea
- eclampsia
Prevention
Ketones in urine can be caused by many factors. If you have ketones in your urine, the first place to look is at your diet. What you eat and drink is very important. You may be able to remedy the situation by making dietary changes, or there may be a more serious cause. See your doctor immediately if you think you might have ketonuria.
Lifestyle Suggestions
Suggestions for ketones in urine:
- Monitor your blood glucose levels.
- Test your ketones regularly.
- Reduce your alcohol consumption.
- Follow a healthy diet plan.