What is Heart Rate?
Heart rate, also known as pulse, is a parameter that determines the number of heart beats per minute (bpm). The heart rate is the number of times the heart beats in a minute, and it may serve as one of indicators of cardiovascular wellness. It plays a significant role in assessing cardiovascular health and overall fitness.
The heart rate can be affected by several factors such as physical exercise, stress levels, emotional state, age, and general well-being. There are also several factors that can influence heart rate, including age, fitness level, and emotional state. A healthy adult typically has a resting heart rate that ranges from 60 to 100 beats per minute, although this may vary depending on individual characteristics.
Consistently observing your heart rate can provide valuable information about your heart wellness condition and enable you to make lifestyle changes to maintain an optimal and balanced heart rate.

Is There a Difference Between your Heart Rate and your Pulse?
Yes, there is a subtle difference between the two. Your heart rate refers to the number of times your heart beats per minute, often measured by placing your fingers on your wrist or neck and counting the beats for 60 seconds. On the other hand, your pulse is the rhythmic expansion and contraction of the arteries in response to the surge of blood pumped by the heart.
Your pulse is the palpable manifestation of your heart rate and is felt as a throbbing sensation in various pulse points throughout your body, including the wrist and neck. Understanding this distinction can be crucial in monitoring your health and fitness levels, as both heart rate and pulse can offer valuable insights into your overall well-being.
What Heart Rate Should I Expect to Have?
The ideal heart rate is dependent on several factors such as age, level of fitness and overall well-being. The norm for most adults is a resting heart rate ranging between 60 and 100 beats per minute (bpm). However, individuals who maintain physical fitness may have resting heart rates towards the lower spectrum of this range. Notably, athletes often exhibit resting heart rates below 60 bpm due to their cardiovascular systems being in good condition.
It should be acknowledged that there's no universal answer regarding the ideal heart rate as it differs between each person.
What's paramount is comprehending your basic level and identifying any significant changes that might require further attention. Consistent physical exercise, a balanced diet, stress management techniques, and adequate rest can all aid in maintaining a healthy heart rate aligned with your individual circumstances.
What is a Good Heart Rate?
In order to determine a healthy heart rate, it is important that it reflects a well-balanced cardiovascular system and is suitable for your health status, age, and level of fitness. Generally, individuals with a resting heart rate between 60 to 100 bpm are considered within the healthy range. However, what constitutes "good" for an individual can be influenced by various factors.
Engaging in regular physical activity can lead to a decrease in your resting heart rate which indicates an improvement in cardiovascular wellness. It is worth noting that differences among individuals are normal and tracking any significant changes over time is paramount.
In the event that your heart rate consistently falls outside of the expected range or if you experience symptoms such as shortness of breath or dizziness, it is highly recommended that you seek advice from a healthcare professional to ensure proper management of your cardiac health.
What is Resting Heart Rate?
Resting heart rate is the count of heart beats per minute while the individual is in a tranquil and composed state, without any physical activity. Resting heart rate can vary significantly and varies from person to person based on factors such as age and fitness level. This measurement serves as one of indicators for one's cardiovascular wellness, and can provide insight into their overall fitness level.
An individual with a lower resting heart rate generally indicates a well-conditioned heart, as it doesn't have to work harder to pump blood. Athletes and people who engage in regular physical exercise usually have lower resting heart rates owing to the efficiency of their cardiovascular systems. Keeping track of changes in your health and fitness by monitoring your resting heart rate over time is key in assessing your heart's well-being.
How to Measure Your Heart Rate?
If you check in with your healthcare practitioner, your doctor will examine your heart rate and rhythm by taking your pulse. Each pulse corresponds to a heartbeat, which pushes blood through your arteries. Knowing your pulse allows your doctor to assess the strength of your blood flow and blood pressure in various places of your body.
Feeling your pulse may tell you how quickly your heart is beating and if it is regular. The amount of times your heart beats in one minute is referred to as your heart rate.
To take your own pulse, do the following:
- Get a watch with a second hand.
- Put your index and middle fingers on the inner wrist of the opposite arm, right below the base of the thumb. Taping or pulsating should be felt against your fingertips.
- Count how many taps you feel in 10 seconds.
- Multiply that figure by 6 to get your heart rate for one minute.
How Do I Use My Pulse to Measure My Heart Rate?
You can utilize a straightforward and accessible technique to calculate heart rate by using their pulse, without any specialized equipment. The first step is to locate a pulse point on the body, commonly found at the wrist (radial pulse) or neck (carotid pulse). Then, use the index and middle fingers to gently apply pressure on the pulse point until you feel a rhythmic throb.
To calculate your heart rate in beats per minute (bpm), count the number of beats felt in 60 seconds. Another option is to count the beats for 15 seconds and multiply it by four to get bpm. Regularly checking your heart rate or pulse, especially at rest, can provide valuable insights into your cardiovascular wellness.
How Do You Measure Your Pulse At Home?
Measuring your pulse at home can be an easy and convenient way to monitor your cardiovascular wellness. Whether you're looking to track your fitness progress or keep an eye on any underlying health conditions, knowing how to measure your pulse accurately is an important skill.
You'll need an analog watch with a second hand (one with a clock face rather than digital numerals). Place your index and middle fingers on the hollow area of your other arm's inner wrist, directly below the base of the thumb.
Your heartbeat should be felt as a tapping or pulse on your fingertips. Examine your watch and count how many taps you feel in 10 seconds. Multiply that figure by 6 to get your heart rate for one minute. A typical pulse rate ranges from 60 to 100 beats per minute.

Measure pulse with a device
A variety of gadgets, including at-home blood pressure units, digital fitness trackers, and smartphone applications may detect your heart rate.
A wireless monitor worn around your chest is the most precise instrument for measuring your heart rate. It communicates with a fitness tracker placed on your wrist.
Digital fitness monitors, at-home blood pressure equipment, and smartphone applications are less precise than manually assessing your heart rate. These gadgets, however, are pretty precise and extremely handy while exercising.
Metal hand grips on exercise machines may be used to monitor your heart rate, although they are often erroneous. Checking your heart rate while exercising is most effective whether done manually or with a digital fitness tracker.
How Do You Measure Your Blood Pressure At Home?
A blood pressure monitor is required to measure your blood pressure at home. Because there are many various types of home blood pressure monitors, you must follow the directions that came with yours.
Some have an arm cuff, while others have a wrist cuff. After 5 minutes of silence, measure in a calm environment. Stay steady while reading and take two or three readings, one to two minutes apart. Make a note of your results.
When at rest, an adult's blood pressure should be less than 120/80. The 120 represents the systolic pressure. The diastolic pressure is 79 millimeters of mercury. A blood pressure measurement of 130/80 or greater is considered high blood pressure, often known as hypertension.
Years of high blood pressure may cause your artery walls to harden and constrict, obstructing blood flow to your heart. It may result in heart disease. Your blood pressure may rise or fall based on your age, heart condition, emotions, exercise level, and medications. A single high result does not indicate that you have high blood pressure. To determine your normal numbers, you must measure them on several occasions while resting.
How to Get Your Heart Rate Up?
Maintaining cardiovascular fitness and overall health necessitates elevating your heart rate. There are various effective ways to accomplish this objective. Engaging in aerobic exercises such as running, swimming, or cycling can significantly increase your heart rate, especially if you're physically active.
Engaging in interval training which involves alternating between high-intensity bursts and periods of rest is another potent method for augmenting heart rate. Additionally, participating in activities like brisk walking, dancing, or stair climbing can help maintain a healthier heart rate.
It is important to commence exercise gradually, particularly if you're new to it, and consult a healthcare professional before making significant modifications to your fitness regimen. By incorporating these strategies into your lifestyle, you can actively improve the vitality of your heart and reap the numerous benefits of a stronger cardiovascular system.

What are Some Causes of an Abnormal Heart Rate?
Here are a few causes:
Dehydration
Your body needs enough water to function properly. Most of the systems in your body, including your circulatory system, cannot perform at their best if you don’t have enough water in your body. It is therefore advisable that you drink at least 8 cups of water a day.
You can tell that your body is dehydrated if you are experiencing these symptoms:
- Low performance when working out
- Changes in your mood
- Fatigue
- Changes in your cognition
Dehydration affects your endothelium functions. The endothelium is the lining in your blood vessels and your heart. In turn, this increases your heart rate and your body's ability to regulate blood pressure.
Ensure that you drink the recommended amount of water daily. Including fruits and vegetables in your diet will also keep you hydrated, as it boosts your intake of fluids.
Not Getting Enough Sleep
Not getting enough sleep or insomnia can also make your heart race. According to the National Health Service (NHS), sleep is one of the primary causes of a racing heart. Here are some symptoms of lack of sleep that you should look out for:
- Feeling fatigued
- Having difficulty concentrating on a task
- Irritability
To get enough sleep every night, you should start following these habits:
- Don't have caffeinated drinks if you are about to go to bed
- Set a bedtime routine and stick to it
- Engage in physical activity during the day
Stress
When you are stressed, your heart rate is more likely to jump. Your body responds to anger, depression, and stress. The way that each person responds to stress will differ from one person to the next. Stress, dehydration, and lack of sleep are common factors that can affect heart rate and disrupt its normal rhythm.
How can you tell if you are stressed and that it is impacting your heart?
- Worrying too much and feeling anxious
- Feeling overwhelmed when working
- Nausea and headaches
- Not getting enough sleep or insomnia
- Increasing heart rate
You can reduce the risk of developing a jumping heart rate by managing your stress levels. Working out, hanging out with friends, and meditating are some of the most effective ways of managing stress.
How can you stop your heart rate from jumping up?
If your heart is racing too often or longer than usual, try following these steps:
- Get enough sleep
- Stop smoking tobacco
- Cut down on alcohol and caffeine
- Pinch your nostrils and blow air through your nose
- Close your eyes and press the eyeballs gently
You are likely to notice that your heart rate is jumping up if you’re stressed. Try following the tips shared here to reduce your stress levels and lower your heart rate. If your jumping heart rate persists, you should always contact your doctor as soon as possible.
When should you contact a medical professional if you have a racing heart?
A jumping heart rate alone doesn’t always mean that there is a problem. It is always important that you seek medical attention if the rhythm of your heart becomes abnormal or causes you any discomfort.
You should contact your medical doctor as soon as possible if you experience these symptoms with a racing heart:
- Pain in the neck, jaw, stomach, and both arms
- Chest pain
- Feeling dizzy
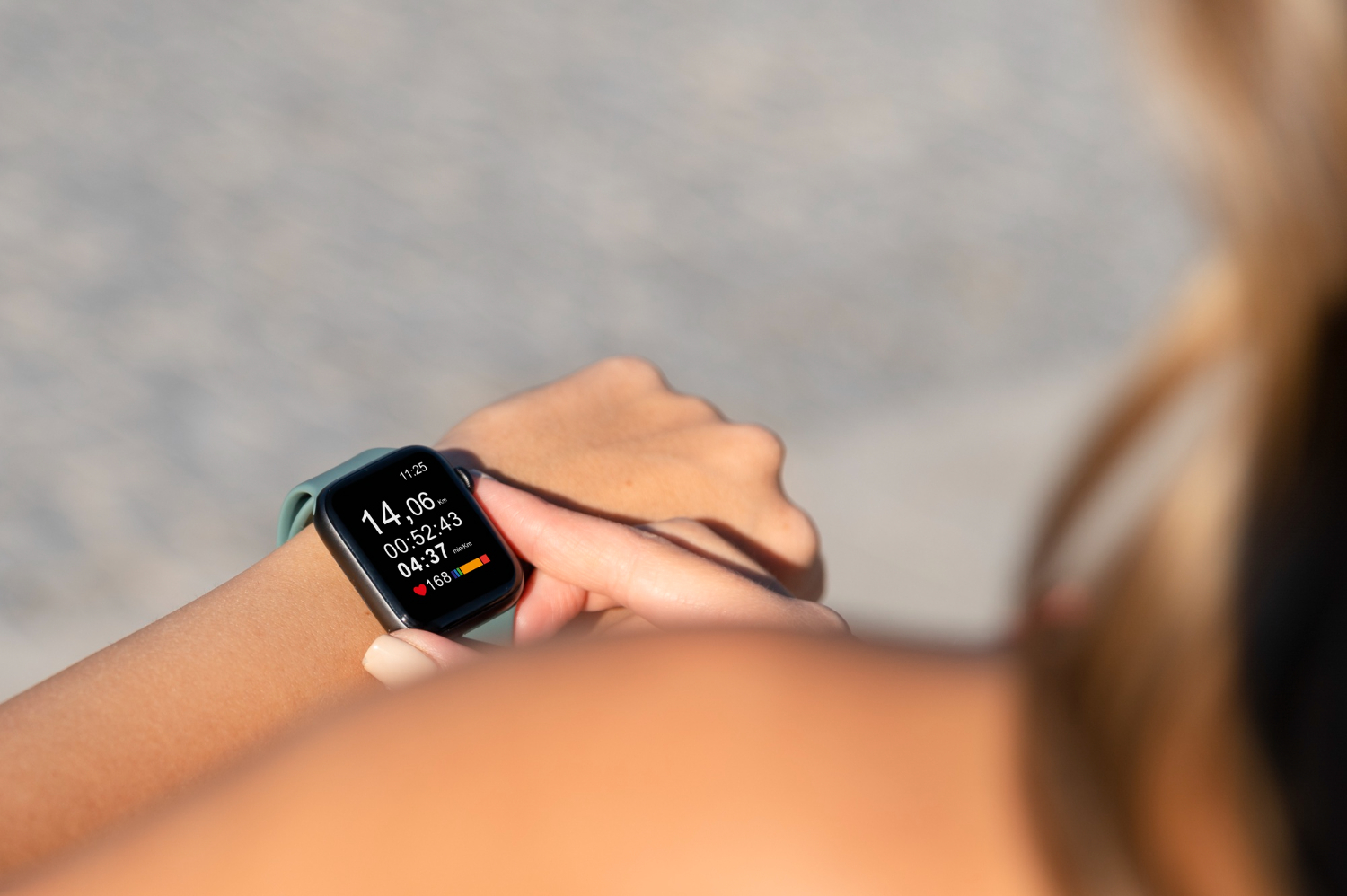

Heart Rate Effect on Sports Performance
Athletes should have the lowest average heart rate compared to the average population. That is, the resting heart rate should be low for maximum endurance on the field.
A young athlete will have a heart rate of about 40-50 beats per minute. During exercise, an athlete’s heart rate can go up to 180-200 bpm.
Exercise strengthens heart muscles, which allows it to pump more blood for every heartbeat. That means more oxygen will be going to the muscles with every heartbeat. If you want to gauge your heart rate intensity, you should first figure out how fast your heart is beating when you are doing some exercise. Your maximum heart rate is the limit of what your cardiovascular muscles can handle when you engage in vigorous physical activity.
Here is a tip you can use when calculating your maximum heart rate. Subtract your age from 220. For instance, if you are 18 years old, you subtract 18 from 220 to get a maximum heart rate of 202. This is the number of times your heart should beat when you engage in a sport activity.
Once you know your maximum heart rate, you can now calculate your desired target heart rate zone. This is the level at which your heart is not being overworked when you are on your feet exercising.
According to the American Heart Association, you should have a target heart rate of 50% -70% of your maximum heart rate when you engage in moderate exercise. When doing vigorous exercise, you should have 70%-85% of your maximum heart rate.
If you are just starting to exercise to get into shape, you should aim for your minimum heart rate zone. You can gradually shift to your maximum heart rate zone if you are healthy and fit. Knowing your target heart rate zones is essential for optimizing your workouts and achieving specific fitness goals.
5 Ways a Heart Rate Monitor Can Optimize Your Training
The following are some ways in which a heart rate monitor can be helpful during a workout. When using a heart rate monitor during your activities, you can track how fast your heart beats and gain other helpful information.
1. Monitor How You Burn Fat
When you exercise, you are burning calories and using energy. As you monitor your heart rate, you can figure out the energy source you are using.
2. Adjust Your Energy Output
The higher your heart rate means you are burning more carbohydrates because your body cannot burn fat fast enough.
Using a heart rate monitor allows you to easily adjust your energy output to match your heart rate during a workout.
3. Know Your Limits
Mastering the art of endurance is crucial if you prefer HIIT workouts. When you put on a heart rate monitor, you can easily determine how far to go in a workout.
You can monitor and maintain your heart rate in any of the heart rate zones. For instance, if you go for low moderate-intensity workouts, you should target between 50-59% heart rate. You should aim at not getting to the red zone, which is 90-99% of the maximum heart rate zone.
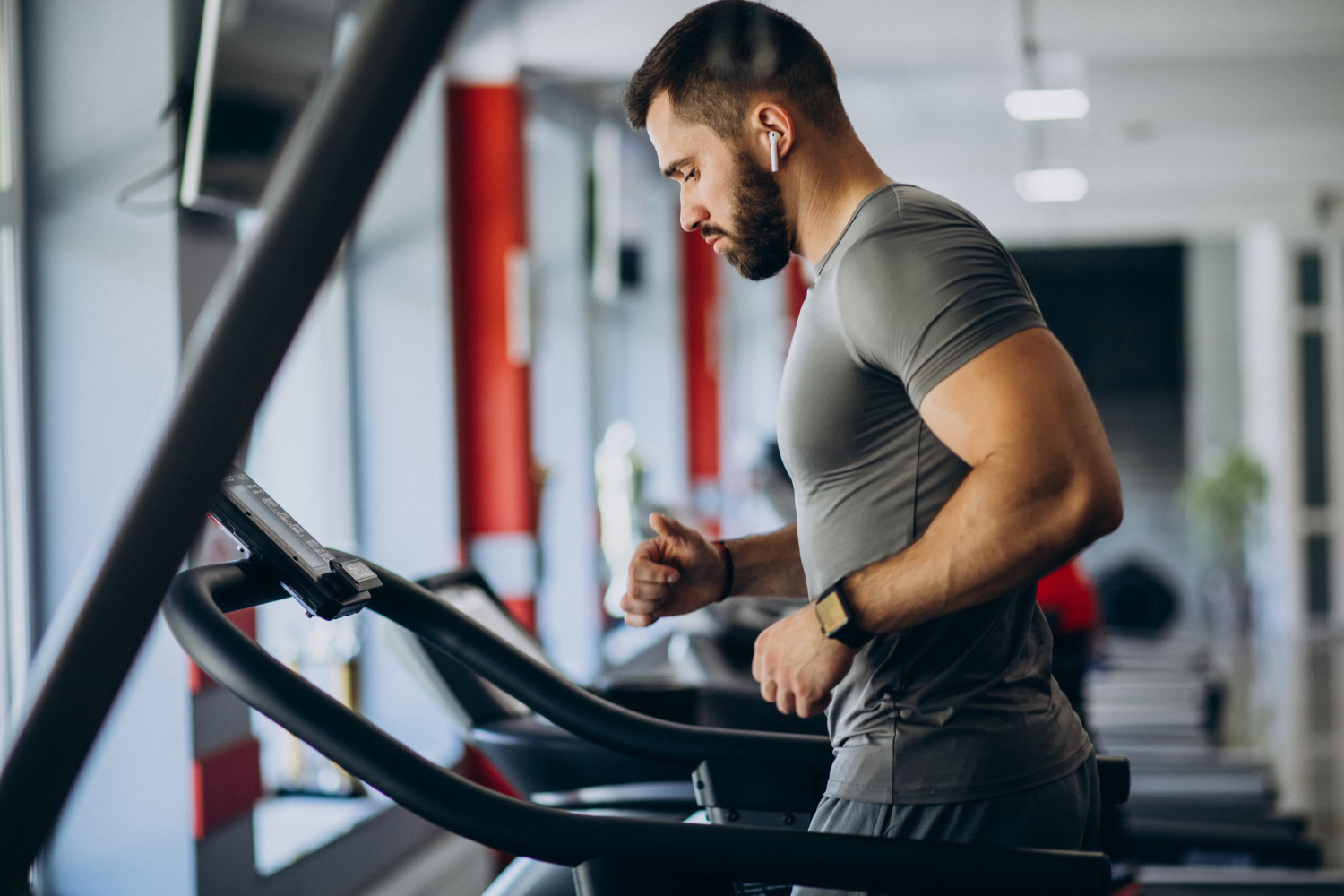

4. Track Your Fitness
With a heart rate monitor, you can easily track your fitness progress. A heart rate monitor will store information from your previous workouts, which means you can easily track your progress over time. You will know if you are on the way to meeting your monthly fitness goals.
5. Challenge Yourself
It is possible to gamify your workouts and make them more entertaining. That means you set a fitness goal and begin to compete against yourself.
With a heart rate monitor, you can watch how your heart beats as you work out or push yourself beyond limits to burn more fat. You can also choose to stay in a particular heart rate zone as long as you want.