Vitamin D is one of the oldest hormones thought to have existed for 750 million years. This hormone, which is in a different form on human skin, turns into vitamin D with the help of sunlight and the liver. It is important to recognize that we haven’t been getting enough sunlight, which is the best source of vitamin D.
Vitamin D deficiency is an important health issue in 50% of the world population. New research shows that vitamin D can help prevent various diseases, such as depression, diabetes, cancer, and heart disease. Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that helps absorb calcium, promoting the growth and mineralization of our bones. Vitamin D also plays a role in various functions of the immune, digestive, circulatory, and nervous systems.
1. What is the Recommended Daily Intake of Vitamin D?
Vitamin D deficiency is a common condition and its prevalence varies by geography. Adult people who have an average level of vitamin D in the blood below 20 ng/dl have a vitamin D deficiency.

Vitamin D requirements vary between 700-1300 mg/day, depending on age mostly. Getting to know vitamin D sources, and knowing how much we can consume, prevents vitamin D deficiency.
Oily seafood
Oily fish and seafood are natural sources of vitamin D. You can meet most of your daily vitamin D requirements with just 3.5 ounces (100 g-670 IU) of cooked salmon.
Vitamin D is also found in other natural sources, such as mackerel, herring, cod liver oil, and salmon.
Fish oil or cod oil meets 62% of your daily vitamin D needs (1 portion= 1 tsp 440 IU)
Tuna meets 32% of your daily vitamin D needs. (1 portion= 168 g 228 IU)

Mushrooms
Mushrooms, just like humans, make their own D vitamins thanks to sunlight. Sunlight-like UV lamps used when producing mushrooms trigger vitamin D2 production. To avoid poisoning, buy the mushroom at the markets. Portobello mushrooms and mushrooms grown with UV light meet half the daily vitamin D needs. (1 portion=1/2 cup 316 IU)
Egg Yolk
Studies show that eggs obtained from chickens grown in pasture contain up to 20% of the daily vitamin D requirement. In general, an egg meets 18% of your daily vitamin D needs. (1 portion= 78 g 44 IU)
Dairy Products
Dairy products are important sources of vitamin D due to the animal fat they contain.
Whole milk provides 18% of your daily vitamin D needs. (1 portion= 1 cup 128 IU)
Yogurt meets 17% of your vitamin D needs depending on its type. (1 portion= 175 g 120 IU)
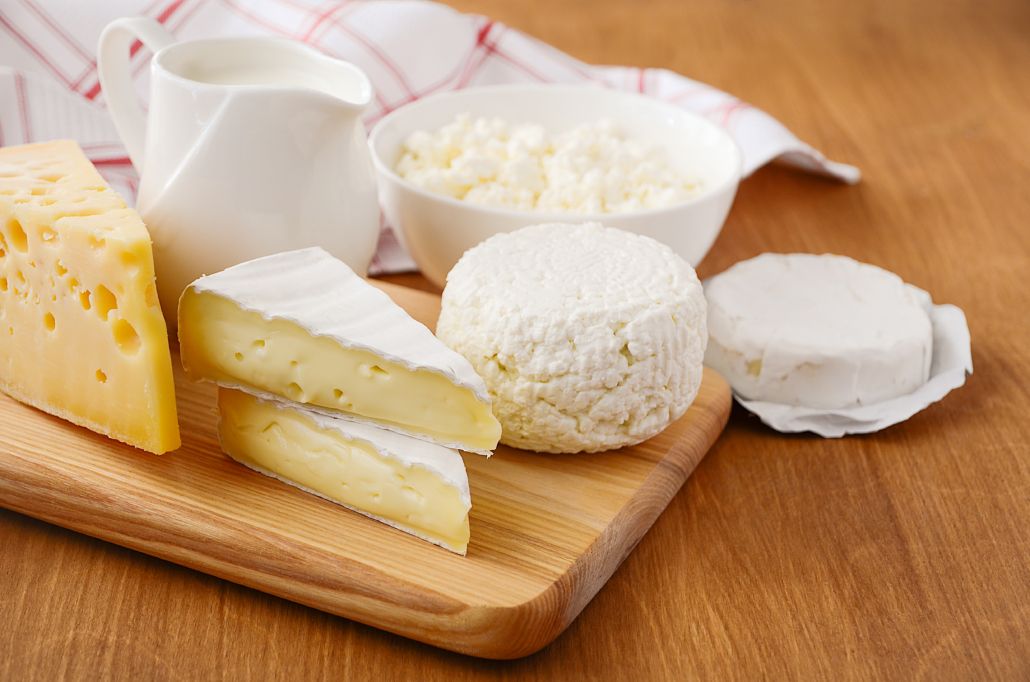

Products Enriched with Vitamin D
Other foods can be enriched with vitamin D because it’s generally in low supply.
Foods such as margarine, cheese, orange juice, soy-almond milk, bread, and cereal are enriched with vitamin D
Soy milk provides 16% of your daily vitamin D needs. (1 portion= 1 cup 116 IU)
Fortified ready-to-eat cereals meet an average of 7% of your daily vitamin D needs. (1 portion=1 cup 56 IU)
Fortified orange juice meets 14% of your daily vitamin D needs. (1 portion= 1 cup 100 IU)
Margarine meets 8.5% of your daily vitamin D needs. (1 portion= 1 tbsp 60 IU)
Some people may need much higher vitamin D doses to raise low vitamin D levels. A qualified healthcare professional must decide on this dose. Otherwise, there may be a risk of vitamin D toxicity.

2. Increasing Sunbathing Time
Vitamin D is called the “sunlight vitamin”. Our body needs sunlight to use vitamin D. Skin type, gender, clothing, nutrition, food supplement use, BMI, and degree of urbanization affect the level of vitamin D in the blood.
Skin color
Melanin pigment in the skin blocks vitamin D. The need for vitamin D increases in people with darker skin because they have more melanin.
Geography
Vitamin D production is high in people who get direct sunlight. There are studies on the differences in vitamin D production in people living in tropical and cold climates.
Clothing
Clothing styles that cover the face, arms, and hands can prevent enough vitamin D intake. Additional exposure to sunlight can increase your vitamin D intake. Just try to avoid the time when the sunlight is most dangerous, between 10 am and 3 pm.

Getting help from supplements
The USDA listed the foods to which vitamin D could be added in 1980 and showed the market availability of these foods. The Food and Drug Administration has paved the way to enrich some foods with vitamin D. These foods are calcium-fortified juice, some cereal and pasta products, yogurt, and some cheese and cheese products. There are two forms of vitamin D: D2 (herbal) and D3 (animal). Supplements allow you to take the vitamin you need with a single dose, but you should consult your doctor. In rare cases, an overdose may occur, causing toxicity.
Vegan
There are two types of vitamin D. Vitamin D2 is a herbal vitamin. If you are a vegan, you can buy vitamin D2 supplements from lichen or mushrooms at specialty stores.