Progesterone is a hormone that is produced by both men and women. It is more important for women since it is connected to menopause, pregnancy, and reproductive health. If you're a woman trying to conceive, you may be interested in raising your progesterone levels. Low levels of progesterone can lead to irregular periods, infertility, decreased sex drive, and other health problems.
A doctor may prescribe several types of progesterone. There are synthetic variants, also known as progestins. Continue reading to discover more about progesterone and how you can increase your levels through certain practices.
What happens when you have low Progesterone?
Fertility problems from low Progesterone
Progesterone plays a critical function in a woman's cycle, ensuring that the uterine lining remains in place for the whole 14-day period. This is done so that a fertilized egg may embed itself in the uterine wall and the pregnancy can develop.
If a woman gets pregnant, her progesterone levels rise, allowing the uterine lining to remain intact. If she does not become pregnant, her progesterone levels fall, causing the uterine lining to shed and her period to begin. However, very low progesterone levels may result in infertility, irregular and heavy periods, and more severe PMS symptoms.
Anxiety from low Progesterone
Progesterone has a significant impact on your mood and functions as an antidepressant. As a result, when it is scarce, it may cause bouts of poor mood, anxiety, and melancholy, as well as sleeplessness.
Estrogen dominance
One of the most common reasons for insufficient progesterone is estrogen dominance. Progesterone and estrogen have a mutually beneficial interaction in which one is required to manage the other. When estrogen levels are too high and progesterone levels are too low, the balance becomes unbalanced, resulting in symptoms such as ovarian fibroids, cellulite, weight gain, painful periods, mood swings, and bloating.

Thyroid Issues
When progesterone levels are low, it can affect the levels of estrogen, which in turn may have an impact on thyroid hormone levels.
Weight Gain
When your body has low levels of progesterone, it may prevent the body from utilizing stored fat as a source of energy. Instead, glucose may be released into the bloodstream, which can potentially result in the breakdown of muscle tissue and the development of cellulite.
How to increase Progesterone levels?
Progesterone is essential for sexual and reproductive health, but it may also have an impact on other parts of your health. Progesterone levels vary for a number of reasons, but they normally decline with age. Progesterone production nearly completely ceases during menopause.
Raising progesterone levels may be beneficial to your health, particularly as you approach perimenopause and menopause. Continue reading to discover more about progesterone and how to increase it.
Diet
Although progesterone is a hormone that cannot be found in food, certain foods may help boost the production of this hormone in the body. Therefore, consuming the right kinds of food can aid in increasing the production of progesterone.
Fiber
As previously mentioned, estrogen and progesterone have a complex relationship, and consuming fiber can potentially help reduce estrogen levels, which may result in increased effectiveness of progesterone. Certain foods contain estrogen, and the longer they take to pass through the digestive system, the more estrogen is absorbed. Fiber can improve bowel movements and reduce the amount of time for estrogen absorption.
Some fiber-rich foods that you can incorporate into your diet are:
- Oats
- Flaxseed
- Quinoa
Adding these foods to your diet may help maintain healthy hormone levels and improve overall digestive health.
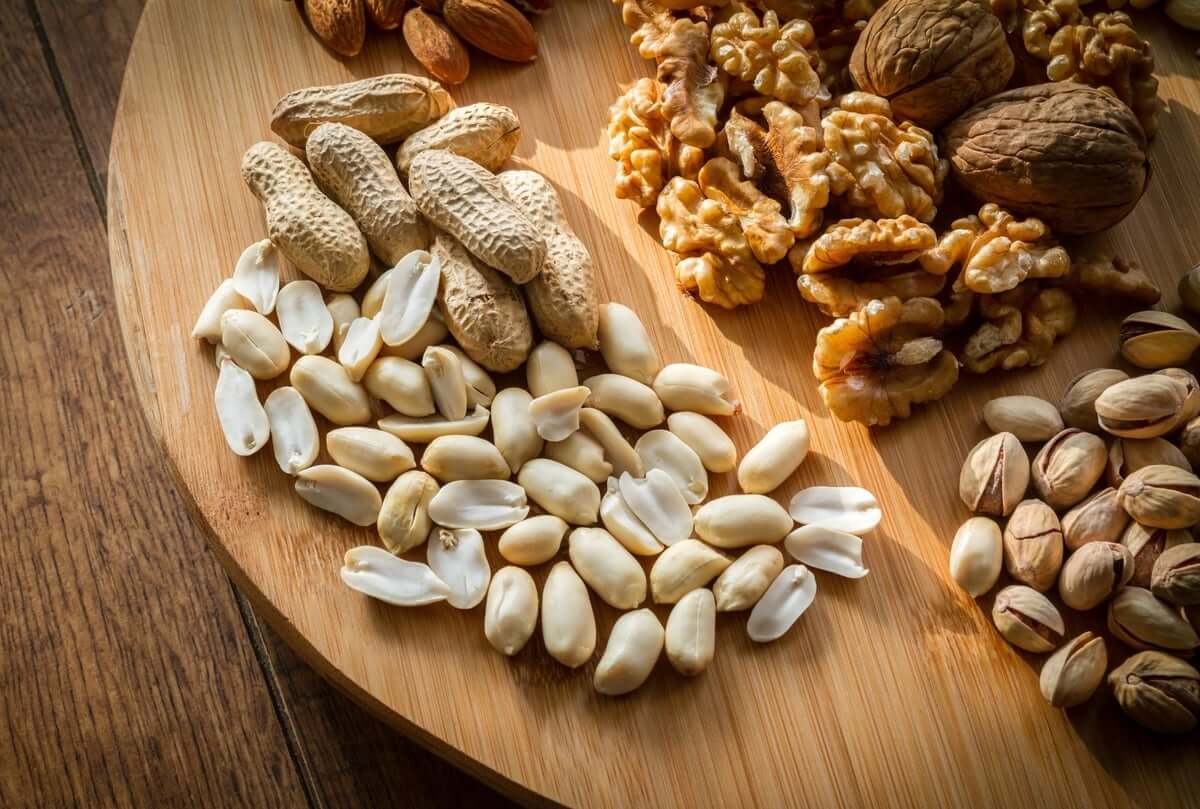

Zinc
Zinc regulates progesterone levels through interacting with the pituitary gland to stimulate the production of FSH. This ensures that the corpus luteum develops and generates progesterone throughout the second part of the menstrual cycle, promoting normal ovulation.
Foods that are high in zinc include oysters, beef, pork, chicken, beans, nuts, and whole grains. Zinc can also be found in smaller amounts in dairy products, seafood, and fortified cereals.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C, may help enhance your progesterone levels naturally. One research found that women who took 750 mg of vitamin C per day had a 77% rise in blood progesterone levels.
Magnesium
Magnesium is a crucial nutrient for regulating hormones and it can aid in increasing progesterone levels. This is due to its role in regulating the pituitary gland, which produces FSH, LH, and TSH hormones that contribute to the production of both estrogen and progesterone. Therefore, consuming foods high in magnesium can be beneficial in boosting progesterone levels.
Here are some examples of magnesium-rich foods that you can incorporate into your diet:
- Spinach
- Fish
- Dark chocolate
- Whole grains
- Nuts and seeds
If you are curious about your Vitamin C intake and magnesium levels why not try Vivoo? Vivoo is an at-home urine test that gives you real-time data on 9 wellness parameters like vitamin C, calcium, magnesium and much more. It only takes 90 seconds to get your results to your smartphone!